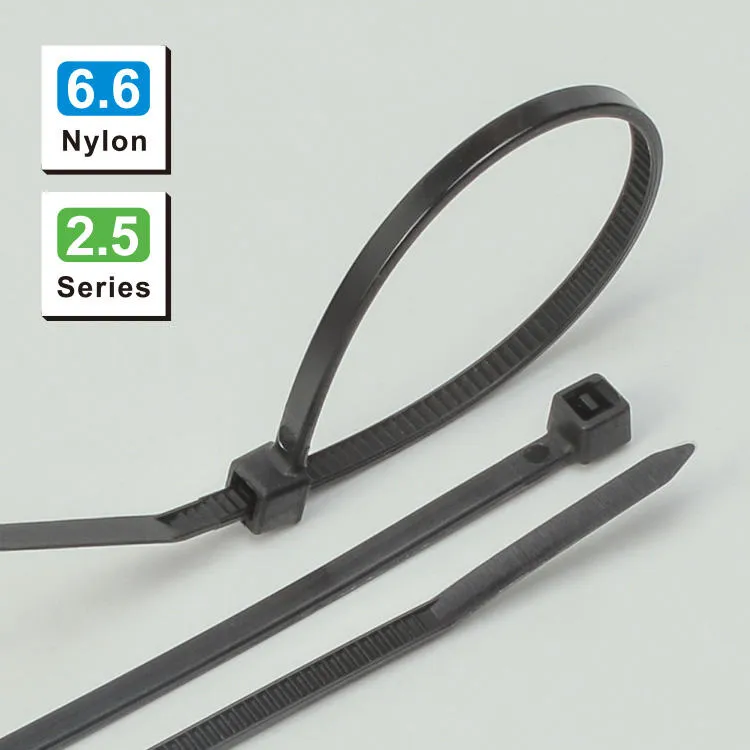
Industrial Cable Tie Selection Guide
In industrial environments, cable ties play a pivotal role in organizing wiring, securing mechanical components, and upholding operational integrity. Their effectiveness relies on meticulous selection based on material properties, technical specifications, and environmental requirements. This guide offers a structured framework for choosing the appropriate cable ties across diverse applications, emphasizing precision and practicality.
1. Material Selection: Core Properties and Applications
The performance of cable ties fundamentally depends on their material composition. Below is a comparative overview of primary materials, their key attributes, and ideal industrial use cases:
| Material | Temperature Range | Key Advantages | Typical Industrial Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon (PA66) | -40°C to 105°C | Cost-efficient, resistant to oils and weak acids | Electronics assembly, general machinery wiring |
| Stainless Steel (304/316) | -200°C to 800°C | Exceptional durability, corrosion/impact resistance | Outdoor infrastructure, chemical plants, marine operations |
| Polypropylene (PP) | -30°C to 120°C | Food-safe, fatigue-resistant | Automotive harnesses, food processing equipment |
| Polyethylene (PE) | -70°C to 80°C | Flexible at low temperatures, non-conductive | Temporary fixes, cold storage, lightweight packaging |
Note: Prioritize certified materials (e.g., FDA for food contact, UL94 for flame retardancy) to ensure compliance with industry standards.
2. Key Specifications for Load and Environment
2.1 Length Calculation
Select a length that allows 10–15% overlap for secure locking.
Example: For a 60mm diameter pipe:Circumference=π×60≈188.5mm⇒Required Length≈188.5×1.15≈217mm (use 250mm standard length).
2.2 Width and Tensile Strength
• Light-Duty (≤3.6mm): Suitable for small bundles (e.g., electronic wires), with tensile strength ≤100N.
• Industrial-Grade (4.8–7.6mm): Ideal for medium loads (100–500N), such as machinery and automotive applications.
• Heavy-Duty (≥9.5mm): Designed for heavy machinery and structural fixes, capable of withstanding ≥1,000N.
2.3 Safety Factor
Always opt for a cable tie with a tensile strength 1.5 times the expected load. For a 300N load, choose a tie rated for ≥450N.

3. Functional Features for Specialized Needs
3.1 Flame Retardancy
Critical in high-risk environments (e.g., power plants), flame-retardant ties should meet UL94 V-0/V-1 standards, ensuring self-extinguishing properties and controlled burn rates.
3.2 UV Resistance
For outdoor applications, use UV-stabilized materials (e.g., nylon with UV additives) to prevent degradation. UV-rated ties can endure 5+ years of direct sunlight.
3.3 Antistatic/Conductive Coatings
In electronics and explosive environments, select ties with:
• Antistatic properties (surface resistance: 10⁶–10¹¹Ω) to mitigate static discharge.
• Conductive properties (surface resistance: <10⁶Ω) for ESD-sensitive areas.
4. Application-Based Selection Scenarios
Scenario 1: Outdoor Electrical Systems
• Challenges: UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, and moisture.
• Solution: 304 stainless steel ties (4.8mm width, 300mm length) with serrated locks to resist loosening in high-wind conditions.
Scenario 2: Food and Beverage Production
• Challenges: Hygiene standards, oil contact, and frequent sanitization.
• Solution: FDA-compliant PP ties (3.6mm width, 200mm length) with smooth surfaces for easy cleaning.
Scenario 3: Heavy Machinery in Chemical Plants
• Challenges: Corrosive chemicals, high pressure, and extreme temperatures.
• Solution: 316 stainless steel ties (9.5mm width, 500mm length) for superior resistance to acids and alkalis.
Scenario 4: Automotive Assembly Lines
• Challenges: Vibration, oil exposure, and fire risks.
• Solution: Flame-retardant nylon ties (UL94 V-2, 2.5mm width) with snap-lock mechanisms for automated installation.
5. Common Pitfalls and Mitigation Strategies
Ignoring Temperature Limits:
• Risk: Nylon degrades at prolonged high heat (>100°C); PP becomes brittle outdoors.
• Mitigation: Use stainless steel for high-temperature zones and UV-stabilized materials for outdoor use.
Underestimating Load Requirements:
• Risk: Inadequate tensile strength leads to failure.
• Mitigation: Apply a 1.5x safety factor and conduct sample testing under simulated conditions.
Neglecting Regulatory Compliance:
• Risk: Non-certified ties violate industry standards (e.g., FDA, RoHS).
• Mitigation: Request material certification reports from suppliers.
6. Maintenance and Replacement Protocols
Inspection Frequency:
• Outdoor ties: Quarterly checks for rust (steel) or cracking (nylon).
• Indoor ties: Biannual inspections for wear and lock functionality.
Replacement Triggers:
• Nylon: Brittleness, lock failure, or discoloration.
• Stainless Steel: Corrosion, deformation, or tensile strength below 70% of the rated value.
Conclusion
Selecting industrial cable ties demands a strategic approach that integrates material science, load analysis, and environmental adaptability. By focusing on core specifications, functional requirements, and application-specific challenges, stakeholders can optimize performance, minimize downtime, and enhance safety. For complex projects, collaboration with suppliers to conduct material testing and validate solutions under real-world conditions is strongly recommended.






